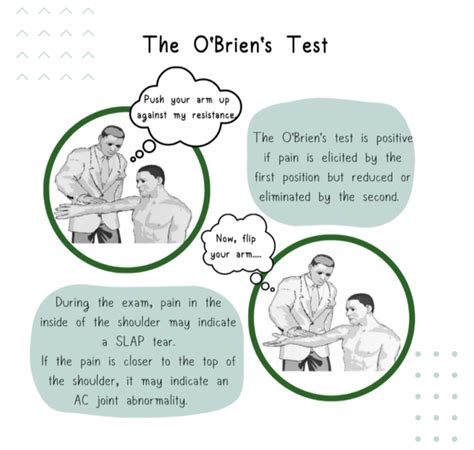
anterior labral tear shoulder test|shoulder labrum tear pain location : company The O’Brien test is a simple procedure that healthcare professionals use to assess shoulder pain. It can detect a cartilage (labral) tear or an acromioclavicular (AC) joint problem. It’s also called the active compression test. This symbol indicates that the safety instructions in the user manual must be observed for the operation of the autoclave. Indicates a hot surface. Do not touch areas marked with this .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Every dental practice should have procedures in place that detail how to handle and disinfect .Autoclave Rental near Phoenix, AZ. Rentals MD carries a vast selection of autoclave sterilizers .
The O’Brien test is a simple procedure that healthcare professionals use to assess shoulder pain. It can detect a cartilage (labral) tear or an acromioclavicular (AC) . See more
Your shoulder is a large and complex joint. The O’Brien test focuses on your AC joint and labrum. Your AC joint is one of four shoulder joints, where two bones . See more
speed's test vs o'brien's
special tests for shoulder labrum
Healthcare providers who may perform the O’Brien test include: 1. Athletic trainers. 2. Orthopedists(bone and joint specialists). 3. Physical therapists. 4. . See moreThe purpose of O'Brien's test also known as the Active Compression Test is to indicate . The O’Brien test is a simple procedure that healthcare professionals use to assess shoulder pain. It can detect a cartilage (labral) tear or an acromioclavicular (AC) joint problem. It’s also called the active compression test.The purpose of O'Brien's test also known as the Active Compression Test is to indicate potential labral (SLAP Lesion) or acromioclavicular lesions as cause for shoulder pain. [1] [2] Technique. With the patient in sitting or standing, the upper extremity to be tested is placed in 90° of shoulder flexion and 10-15° of horizontal adduction.
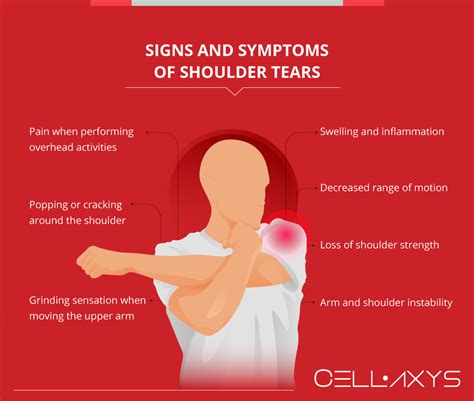
A Review of the Special Tests Associated with Shoulder Examination: Part II: Laxity, Instability, and Superior Labral Anterior and Posterior (SLAP) Lesions. The American Journal of Sports Medicine. 2003;31(2):301-307.The labrum can tear a few different ways: 1) completely off the bone, 2) within or along the edge of the labrum, or 3) where the bicep tendon attaches. Diagnosing a labrum tear involves a physical examination and most likely an MRI, CT scan and/or arthroscopy of the shoulder.Diagnosing Labral Tears of the Shoulder. To evaluate for a possible shoulder labrum tear, a Penn orthopaedic specialist will examine your shoulder, conduct several physical tests to check your range of motion, take a full health history and discuss any past injuries you may have had. The labrum is the attachment site for the shoulder ligaments and supports the ball-and-socket joint as well as the rotator cuff tendons and muscles. It contributes to shoulder stability and, when torn, can lead to partial or complete shoulder dislocation.
O’Brien’s Test is a special orthopaedic/orthopedic test for the shoulder that attempts to test specifically for glenohumeral joint labral tears (and more specifically for SLAP Lesions; superior labral tear from anterior to posterior).Imaging Tests. Your doctor may order an MRI scan to determine whether you have a shoulder labral tear or another type of injury causing your symptoms, such as a fracture or torn rotator cuff. The scan may be accompanied by an injection of contrast dye into the joint to help detect injury to the shoulder labrum.For example, orthopaedic surgeons can now use miniaturized instruments and cameras (arthroscopic surgery) to see inside a joint. This enables them to identify and treat a shoulder injury called a glenoid labrum tear, also known as a labral tear.
A shoulder labral tear is an injury to the ring of cartilage in the shoulder joint. Two of the most common tears are the SLAP (Superior Labral tear form Anterior to Posterior) tear and the Bankart tear. Some kinds of labral tears - especially a Bankart lesion - can increase the potential for shoulder dislocations. The O’Brien test is a simple procedure that healthcare professionals use to assess shoulder pain. It can detect a cartilage (labral) tear or an acromioclavicular (AC) joint problem. It’s also called the active compression test.The purpose of O'Brien's test also known as the Active Compression Test is to indicate potential labral (SLAP Lesion) or acromioclavicular lesions as cause for shoulder pain. [1] [2] Technique. With the patient in sitting or standing, the upper extremity to be tested is placed in 90° of shoulder flexion and 10-15° of horizontal adduction.
A Review of the Special Tests Associated with Shoulder Examination: Part II: Laxity, Instability, and Superior Labral Anterior and Posterior (SLAP) Lesions. The American Journal of Sports Medicine. 2003;31(2):301-307.The labrum can tear a few different ways: 1) completely off the bone, 2) within or along the edge of the labrum, or 3) where the bicep tendon attaches. Diagnosing a labrum tear involves a physical examination and most likely an MRI, CT scan and/or arthroscopy of the shoulder.Diagnosing Labral Tears of the Shoulder. To evaluate for a possible shoulder labrum tear, a Penn orthopaedic specialist will examine your shoulder, conduct several physical tests to check your range of motion, take a full health history and discuss any past injuries you may have had. The labrum is the attachment site for the shoulder ligaments and supports the ball-and-socket joint as well as the rotator cuff tendons and muscles. It contributes to shoulder stability and, when torn, can lead to partial or complete shoulder dislocation.
shoulder labrum tear pain location
O’Brien’s Test is a special orthopaedic/orthopedic test for the shoulder that attempts to test specifically for glenohumeral joint labral tears (and more specifically for SLAP Lesions; superior labral tear from anterior to posterior).Imaging Tests. Your doctor may order an MRI scan to determine whether you have a shoulder labral tear or another type of injury causing your symptoms, such as a fracture or torn rotator cuff. The scan may be accompanied by an injection of contrast dye into the joint to help detect injury to the shoulder labrum.For example, orthopaedic surgeons can now use miniaturized instruments and cameras (arthroscopic surgery) to see inside a joint. This enables them to identify and treat a shoulder injury called a glenoid labrum tear, also known as a labral tear.
positive shoulder labral tear test
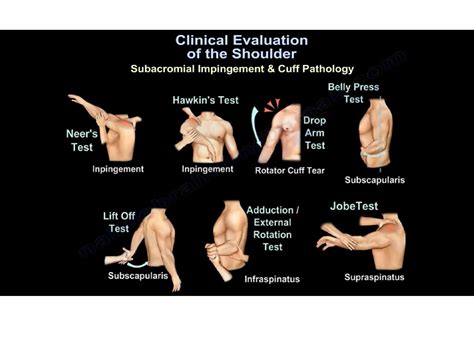
positive shoulder impingement test
positive o'brien's test shoulder
how to tell if you tore your rotator cuff
The application of pressure increases the temperature at which water boils, allowing steam to reach temperatures above the normal boiling point and exert greater force on the surfaces being sterilized.
anterior labral tear shoulder test|shoulder labrum tear pain location